Is It Easy to Confuse Bone Cancers and Liver Cancer
Metastatic liver cancer is a cancer that has spread to the liver from elsewhere in the body.
-
Weight loss and a poor appetite may be the first symptoms.
-
Doctors base the diagnosis on results of blood tests and usually biopsy.
-
Chemotherapy drugs and radiation therapy may help relieve symptoms but do not cure the cancer.
Metastatic liver cancer most commonly originates in the lungs Overview of Lung Tumors Lung tumors can be Noncancerous Cancerous All lung tumors require medical evaluation because even noncancerous tumors can cause problems if they grow and block breathing. The treatment of lung... read more , breasts Breast Cancer Breast cancer occurs when cells in the breast become abnormal and divide uncontrollably. Breast cancer usually starts in the glands that produce milk (lobules) or the tubes (ducts) that carry... read more  , large intestine Colorectal Cancer Family history and some dietary factors (low fiber, high fat) increase a person's risk of colorectal cancer. Typical symptoms include bleeding during a bowel movement, fatigue, and weakness... read more
, large intestine Colorectal Cancer Family history and some dietary factors (low fiber, high fat) increase a person's risk of colorectal cancer. Typical symptoms include bleeding during a bowel movement, fatigue, and weakness... read more  , pancreas Pancreatic Cancer Smoking, chronic pancreatitis, male sex, being black, and possibly long-standing diabetes are risk factors for pancreatic cancer. Abdominal pain, weight loss, jaundice, and vomiting are some... read more , or stomach Stomach Cancer A Helicobacter pylori infection is a risk factor for stomach cancer. Vague abdominal discomfort, weight loss, and weakness are some typical symptoms. Diagnosis includes endoscopy and biopsy... read more
, pancreas Pancreatic Cancer Smoking, chronic pancreatitis, male sex, being black, and possibly long-standing diabetes are risk factors for pancreatic cancer. Abdominal pain, weight loss, jaundice, and vomiting are some... read more , or stomach Stomach Cancer A Helicobacter pylori infection is a risk factor for stomach cancer. Vague abdominal discomfort, weight loss, and weakness are some typical symptoms. Diagnosis includes endoscopy and biopsy... read more  . Leukemia Overview of Leukemia Leukemias are cancers of white blood cells or of cells that develop into white blood cells. White blood cells develop from stem cells in the bone marrow. Sometimes the development goes awry... read more (a cancer of white blood cells) and lymphoma Overview of Lymphoma Lymphomas are cancers of lymphocytes, which reside in the lymphatic system and in blood-forming organs. Lymphomas are cancers of a specific type of white blood cells known as lymphocytes. These... read more
. Leukemia Overview of Leukemia Leukemias are cancers of white blood cells or of cells that develop into white blood cells. White blood cells develop from stem cells in the bone marrow. Sometimes the development goes awry... read more (a cancer of white blood cells) and lymphoma Overview of Lymphoma Lymphomas are cancers of lymphocytes, which reside in the lymphatic system and in blood-forming organs. Lymphomas are cancers of a specific type of white blood cells known as lymphocytes. These... read more  (a cancer of the lymph system), especially Hodgkin lymphoma Hodgkin Lymphoma Hodgkin lymphoma is a cancer of a type of white blood cell called lymphocytes and is distinguished from other lymphomas by the presence of a particular kind of cancer cell called a Reed-Sternberg... read more , may involve the liver.
(a cancer of the lymph system), especially Hodgkin lymphoma Hodgkin Lymphoma Hodgkin lymphoma is a cancer of a type of white blood cell called lymphocytes and is distinguished from other lymphomas by the presence of a particular kind of cancer cell called a Reed-Sternberg... read more , may involve the liver.
Cancers spread to the liver because the liver filters most of the blood from the rest of the body, and when cancer cells break away from a primary cancer, they often enter and travel through the bloodstream. Sometimes the discovery of metastatic liver cancer is the first indication that a person has cancer.
Often, the first symptoms are vague. They include weight loss, poor appetite, and sometimes fever. Typically, the liver is enlarged and hard. It may feel tender and often lumpy. Occasionally, the spleen is enlarged. At first, unless the cancer is blocking the bile ducts, the person has mild or no jaundice Jaundice in Adults In jaundice, the skin and whites of the eyes look yellow. Jaundice occurs when there is too much bilirubin (a yellow pigment) in the blood—a condition called hyperbilirubinemia. (See also Overview... read more  (a yellowish discoloration of the skin and the whites of the eyes). Later, the abdomen may become swollen (distended) with fluid (a condition called ascites Ascites Ascites is the accumulation of protein-containing (ascitic) fluid within the abdomen. Many disorders can cause ascites, but the most common is high blood pressure in the veins that bring blood... read more ).
(a yellowish discoloration of the skin and the whites of the eyes). Later, the abdomen may become swollen (distended) with fluid (a condition called ascites Ascites Ascites is the accumulation of protein-containing (ascitic) fluid within the abdomen. Many disorders can cause ascites, but the most common is high blood pressure in the veins that bring blood... read more ).
-
Liver imaging tests
Doctors may suspect metastatic liver cancer in people who lose weight and have an enlarged liver or who have a cancer that tends to spread to the liver. However, doctors often have difficulty diagnosing the cancer until it is advanced.
If doctors suspect liver cancer, liver tests, which are simple blood tests, are done to evaluate how well the liver is functioning. Results may be abnormal, as they are in many disorders. Thus, this finding cannot confirm the diagnosis. Ultrasonography is usually helpful, but computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the liver are usually more accurate in detecting the cancer. Before CT or MRI is done, a contrast agent Radiographic Contrast Agents During imaging tests, contrast agents may be used to distinguish one tissue or structure from its surroundings or to provide greater detail. Contrast agents include Radiopaque contrast agents... read more is injected into a vein. The contrast agent helps make abnormalities, if present, easier to see (see Imaging Tests of the Liver and Gallbladder Imaging Tests of the Liver and Gallbladder Imaging tests of the liver, gallbladder, and biliary tract include ultrasonography, radionuclide scanning, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography... read more ). However, imaging tests cannot always detect small tumors or distinguish cancer from cirrhosis Cirrhosis of the Liver Cirrhosis is the widespread distortion of the liver's internal structure that occurs when a large amount of normal liver tissue is permanently replaced with nonfunctioning scar tissue. The scar... read more 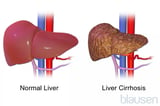 or other abnormalities.
or other abnormalities.
-
Chemotherapy
-
Radiation
-
Surgery
Treatment depends on how far the cancer has spread and what the primary cancer is. Options include the following:
-
Chemotherapy drugs: These drugs may be used to temporarily shrink the tumor and prolong life, but they do not cure the cancer. Chemotherapy drugs may be injected into the liver's main artery (the hepatic artery), delivering a large amount of the drugs directly to the cancer cells in the liver. With this method, the rest of the body is less exposed to the drugs, and thus side effects are fewer and milder.
-
Radiation therapy to the liver: Sometimes this treatment reduces severe pain caused by advanced cancer, but it has little other benefit.
-
Surgery: If only a single tumor or a few tumors are found in the liver, they may be surgically removed, especially if they originated in the intestines. However, not all experts consider this surgery worthwhile.
The following are some English-language resources that may be useful. Please note that THE MANUAL is not responsible for the content of these resources.
-
American Cancer Society: Provides comprehensive information about liver cancer, including its symptoms, diagnosis, staging, and survival rates.
-
American Liver Foundation: Hosts community education programs that give an overview of all aspects of liver disease and wellness. Also provides access to support groups, information on finding a physician, and opportunities to participate in clinical trials.
CLICK HERE FOR THE PROFESSIONAL VERSION

Copyright © 2022 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Source: https://www.msdmanuals.com/en-sg/home/liver-and-gallbladder-disorders/tumors-of-the-liver/metastatic-liver-cancer
0 Response to "Is It Easy to Confuse Bone Cancers and Liver Cancer"
Post a Comment